Hair transplant surgery is a common option for persons who are experiencing hair loss. Scarring is possible following a hair transplant, as with any surgical operation. This blog post will look at the many reasons of scarring following a hair transplant and what you can do to limit the risk of scarring and ensure a healthy outcome.
The Two Types of Scarring After Hair Transplant
Scarring following a hair transplant can be classified into two types: hypertrophic scarring and keloid scarring. When the incision site becomes elevated and red, and then it flattens out over time, resulting in hypertrophic scarring. In contrast, keloid scarring develops when the incision site becomes elevated, thick, and may continue to expand beyond the incision site.
Factors That Contribute to Scarring After Hair Transplant
Scarring following a hair transplant can be caused by a number of circumstances, including:
Genetics: Some people are predisposed to having scars due to their ancestors.
Age: As we become older, our skin loses elasticity, making us more prone to scarring.
Skin Color: People with darker skin are more likely to develop keloid scarring.
Surgery Technique: The type of hair transplant technique employed can influence the likelihood of scarring. The FUT (follicular unit transplant) procedure, for example, entails removing a strip of skin, which can result in a linear scar. In contrast, the FUE (follicular unit extraction) method involves extracting individual hair follicles, which lowers the risk of scarring.
Aftercare: Aftercare is critical for lowering the risk of scarring following a hair transplant. This includes following your healthcare provider’s recommendations, keeping the incision site clean and covered, and avoiding activities that can put stress on the incision site.
How to Reduce the Risk of Scarring After Hair Transplant?
Hair transplant surgery is a common option for persons who are experiencing hair loss. Scarring, on the other hand, is a common issue for many patients, and the sort of hair transplant operation you choose can influence your risk of scarring.
FUT Hair Transplant
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT) entails taking a strip of skin from the back of the head and separating it into individual hair follicles. The transplanted hair follicles are subsequently placed in the balding area. This procedure results in a linear scar on the back of the head where the skin strip was removed. The scar is visible if the hair is cut very short, however it can be disguised if the hair is cut longer.
FUE Hair Transplant
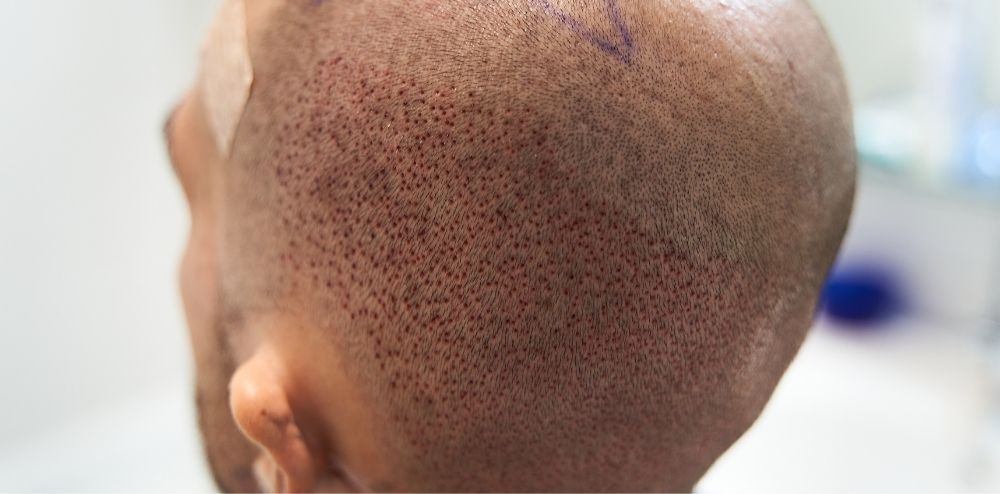
The FUE (follicular unit extraction) method, on the other hand, entails punching individual hair follicles from the back of the head. The transplanted hair follicles are subsequently placed in the balding area. Because the individual hair follicles are eliminated one by one, there is no need to remove a strip of skin, this approach does not produce a linear scar. Instead, tiny spots will appear on the back of the head where individual hair follicles were plucked. These dots are normally quite little, disappear over time, and can be concealed by hair.
Why Is There a Scar After FUT But Not After FUE?
The scar after FUT hair transplant is simply because the FUT procedure includes removing a strip of skin, whereas the FUE method involves removing individual hair follicles one by one. When removing a strip of skin, the incision site must be closed, which may result in a linear scar. Individual hair follicle removal, on the other hand, eliminates the need to seal an incision site, lowering the danger of scarring.
You can lessen the risk of scarring after a hair transplant by doing the following steps:
Select an experienced hair transplant specialist: Check that the personnel at your preferred hair salon has the requisite abilities and experience to conduct the treatment safely and successfully.
Choose the right technique: As previously stated, the FUE procedure involves eliminating individual hair follicles, which decreases the danger of scarring. In addition, unlike the FUT procedure, DHI and Sapphire FUE do not leave any linear scars.
Follow aftercare instructions: Following aftercare guidelines is critical for lowering the risk of scarring following a hair transplant. Make sure to follow your healthcare provider’s directions.
Use topical medicines that your doctor has advised to help decrease the appearance of scars.
Finally, scarring following a hair transplant is a common problem. Scarring can be caused by a variety of variables, including genetics, age, skin type, surgical method, and aftercare. Choose an experienced hair transplant team, follow proper aftercare guidelines, and explore topical treatments if necessary to lessen the risk of scarring. You can get a successful hair transplant and enjoy a thicker, healthier head of hair with the correct care and attention.